Blockchain Innovation Technology
Why is Blockchain here to stay and to be the technology of innovation? Because it will be possible in the very near future to make several creations related not only to the world of technology or banking transactions, but of all human innovations. In it we will have great development possibilities to meet needs in general, for example in agribusiness, industries, stock exchange, economy in general, etc.
Blockchain comes as a world of opportunities for large technology corporations and everyday events in general, it is a technology that is growing and that many companies are still discovering how it is possible to use it to meet significantly important points of how to add value to the business.
Definition
In the definition, the most suitable for Blockchain would be “Distributed registration technology that aims at decentralization as a security measure” or it can also be “the protocol of trust” or also a more standardized “Distributed database that keeps a permanent transaction record and the proof of violation”, among them whatever the best definition they are all linked to the future and that will change the way of doing and functioning of many things and people.
Creation
The creation of Blockchain came along with a source code for another technology that emerged in mid-2008, bitcoin. Blockchain was inserted into the original source code of bitcoin and published by Satoshi Nakamoto in the article “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System”.
Since then, technologies have continued to be developed and commercialized and Blockchain has become the basis of cryptocurrencies that have emerged from 2008 to the present day, and then the new nomenclatures (versions) “Blockchain 2.0” have emerged, aimed at be closer to a distributed blockchain database project, “Ethereum” this is already a slightly more comprehensive version called “decentralized autonomous organizations” (DAO), virtual companies based only on a set of rules from this new generation of blockchain.
Blockchain has received interest from banks, companies and government organizations. Since then, modifications have been made from the original version and new applications have been linked to the blockchain.
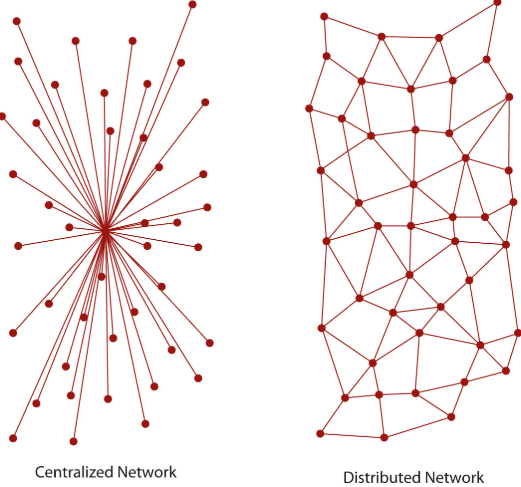
Peer-to-Peer
Like the acronym P2P, a computer network architecture where each setting works as a normal computer (client) or as a server, allowing the exchange of information or services without the need for a central computer to carry out the transaction. A well-known example of peer-to-peer is Torrents.
Decentralization
Decentralization is characterized when an absolute power, whatever it may be, becomes a clear and faster example to understand today would be our model of bank transactions, where everything we are going to do regarding payments and receipts that involve a type of currency are linked to a banking institution.
Decentralization in this example would be the withdrawal of the institution from the middle of the transaction where we would make a direct transfer without depending on the institution, without charging any type of charge, without difficulty and with security.
1 Figure example Network
Blocks and Transactions
On January 3, 2009, at 18:15:05, a certain Satoshi Nakamoto generated the genesis block of Bitcoin. The inventor’s identity remains unknown to this day.
50 Bitcoins were generated in the genesis block. Its hash partly consisted of the following text: “The Times 03 / Jan / 2009 Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks”. The phrase was taken from the headline of an article in the British edition of The Times. The article dealt with how UK Finance Minister Alistair Darling was forced to consider further measures to save banks in the midst of an economic crisis.
The launch of the Bitcoin network was preceded by the publication dated October 31, 2008, of a document describing the protocol and operating principle of the payment system in the form of a Peer-to-Peer network. According to Satoshi, the development of the new payment system began in 2007.
The first Bitcoin transaction took place on January 12, 2009 – on that day, Satoshi Nakamoto sent 10 BTC to Hal Finney. Three days before that, the launch of Bitcoin v 0.1 was published.
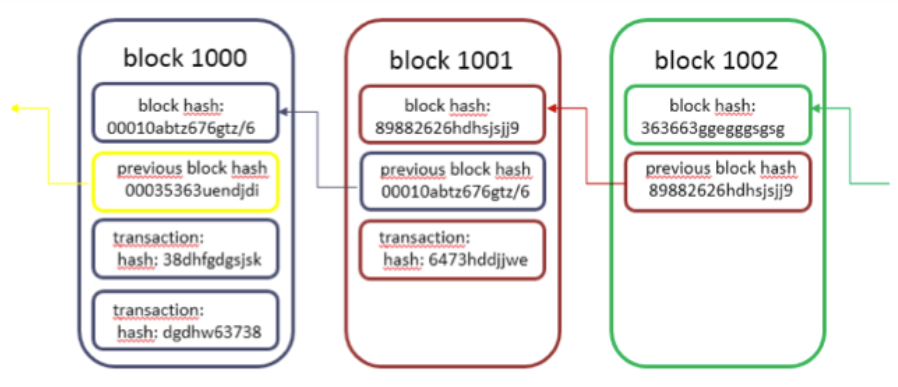
The genesis block is coded in the software and serves as the initial state of the system. It can contain information about the rules or instructions about the remaining database.
That done, the database is formed from a series of blocks that together form a chain. This is where the name ‘chain of blocks’ (Blockchain) comes from. Each block in the chain contains information or transactions. As transactions are added, your information is stored in the block according to the time it was processed. This combination of information and time creates a ledger that documents value or other resources in the database.
After the transactions are stacked on the block, a signature or “hash” is added to the end of the block. The hash is linked to the previous block in the chain. These hashes form the links going back between the strings until they reach the genesis block. The hash includes the current block number and the next block number in the chain. It also includes the date and time it was signed, in addition to the number of transactions included in the present block. The hash is presented as an encrypted key.
2 Figure Hash Block example
Consensus Algorithm
And finally we arrived at the consensus Algorithm, I believe that the most important point of the technology, which proves the security and the guarantee that the transaction will be carried out and with due guarantees. In Blockchain the consensus algorithm is used to solve the trust problem, where no data can be erased and the inserts must be believed by everyone.
It can only be considered that a new block has been created if it meets “also” the rule defined by the Consensus Algorithm, therefore, the new block is included in the Blockchain, making the new data public.
Another important point is that the definition of a Consensus Algorithm means that decisions about what will be inserted in the Blockchain do not depend on any centralizing entity, thus guaranteeing its independence.
In this way, each user of the network has the ability to verify the block’s authenticity in the Blockchain, creating in more brief terms the Security necessary for this great technology to take immeasurable proportions and can be of great use for new businesses and for humanity in general.
The transformation
The transformation is already taking shape in several fields that we cannot yet imagine, but it is already among us.
The state of California has an idea of a proposal made by the governor, who suggested that large corporations pay for the use of their consumers’ data. This would be entirely possible with the creation of a technology made with Blockchain to control all of this.
A large supermarket chain recently announced that it will use blockchain to improve food security. With conventional technology, it took about a week to trace the origin of the contaminated products back to the farm it came from, but with the blockchain the network managed to reduce it to 2.2 seconds.
The healthcare area has been presenting several innovations that use blockchain technology in the development of new solutions. One of these is currently the electronic medical record, the main idea of managing data related to the health of the population, where work was started to share and integrate this health data, which is considered crucial to improve the quality of health services, reduce medical costs and accelerate research.
However, these records are distributed in hospitals and clinics with decentralized and private systems, and the sharing of data and the transit of this data to consolidate information represents a risk to patients’ privacy. To solve this problem, Blockchain together with smart contracts can improve the interoperability of health data, since all transactions are validated through the consensus algorithm and no participant can modify the data arbitrarily.
Going further, and in an environment still in my view, little explored but with spontaneous growth Blockchain makes a perfect union with IoT (Internet of Things). The Internet of Things (IoT) is a fast-growing industry designed to transform homes, cities, farms, factories and just about everything making them smart and more efficient. According to Gartner, by 2020, there will be more than 20 billion connected things worldwide, fueling a market that will be worth at least $ 3 trillion.
However, chaotic growth will bring many challenges such as identifying, connecting, protecting and managing so many devices.
This is something that perhaps can be resolved through Blockchain, the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, which is proving its value in many other industries, including IoT.
Blockchain will allow the creation of more secure network meshes, in which IoT devices reliably interconnect, avoiding threats such as device spoofing and impersonation.
Although still in its early stages of development, IoT is composed mainly of technologies that allow data collection, remote monitoring and device control. As we move forward, the IoT will become a network of autonomous devices that can interact with each other and with their environment and make smart decisions without human intervention.
This is where Blockchain can shine and form the foundation that will support a shared economy based on machine-to-machine (M2M) communications.
The incredible number of opportunities and paths to be explored within this context makes us believe that continuous improvement depends on us, uniting our strengths and the expectations of large corporations, making the possibility and the gratification of being able to participate in everything increasingly unique.